Business Classification
| District Cooling and Heating | Supply of electricity or heat for heating, hot water, or cooling purposes to houses, shopping complexes, and other buildings in a certain area |
|---|---|
| Industrial Complexes | Supply of industrial electricity or heat to companies in industrial complexes |
Concept Map
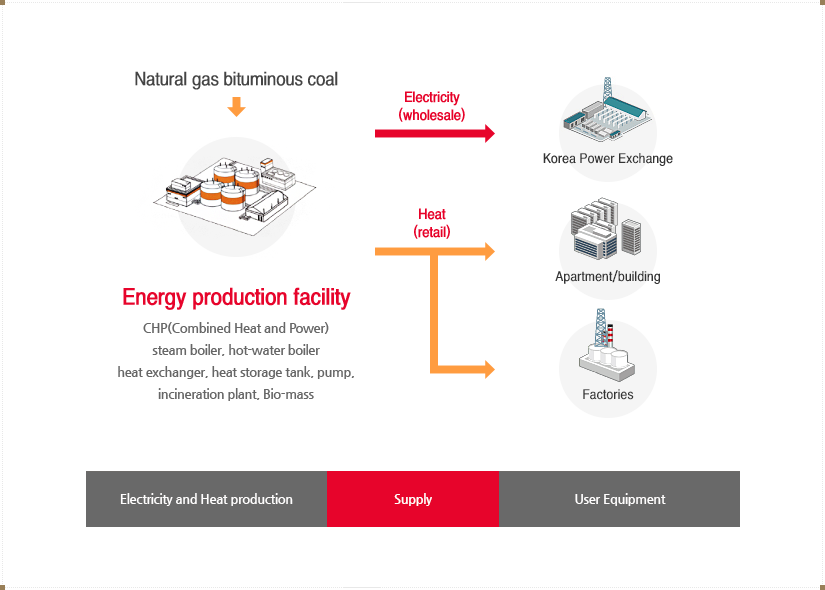
District Energy facilities use fuels such as LNG and bituminous coal to generate heat and electricity. The heat produced is directly supplied to apartments, buildings, etc. for heating purposes or industrial purposes for businesses.
The electricity produced is sold to Korea Power Exchange. Because the District Energy business produces both heat and energy, it has the characteristics of both the city gas distribution business and the Power Business business.